Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (SCCM), formerly System Center Configuration Manager, and Intune are popular Microsoft tools for managing and deploying software and devices in an organization.
While both tools serve similar purposes, there are some key differences. Let's explore those differences to help you determine which tool is best for your organization's needs.
What is SCCM?
SCCM is a software management tool that allows organizations to manage and deploy software and devices across their network. It is a part of the Microsoft System Center suite and is commonly used to manage large-scale deployments.
SCCM has many features that provide IT professionals with the tools to oversee software installations, updates, and configurations across multiple workstations and servers, ensuring that every network component complies with the organization's policies and standards.
Key Features of SCCM
- Software Distribution: Allows IT teams to deploy software to devices simultaneously, making it easier to manage large-scale operations
- Patch Management: IT teams can quickly deploy patches and updates to devices across their network, ensuring that all devices are up-to-date and secure
- Operating System Deployment: Allows for easy deployment of operating systems to new devices, making it easier for employees to set up new devices
- Remote Control: Enables IT teams to access and control devices remotely, making it easier to troubleshoot issues and support employees
- Reporting and Monitoring: Provides detailed reporting and monitoring capabilities, allowing IT teams to track the status of their deployments and identify any issues that may arise
What is Intune?
Microsoft Intune is designed for organizations seeking a flexible and scalable cloud-based device management solution that supports a remote and mobile workforce. It's optimal for managing various devices and applications across various platforms, including Windows, iOS, Android, and macOS, from anywhere in the world.
Intune facilitates mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM), allowing IT administrators to enforce security policies and conduct remote actions like wiping data on lost devices.
Key Features of Intune
- Device Management: Allows IT teams to manage and secure devices that are used by employees, including mobile devices, laptops, and desktops
- Application Management: IT teams can manage and deploy applications to devices, ensuring employees can access the tools they need to do their jobs
- Conditional Access: Enables teams to set policies controlling access to corporate resources based on device compliance and user identity
- Integration with Other Microsoft Tools: Integrates with other Microsoft tools, such as Autopilot Active Directory and Office 365, to provide a comprehensive device management solution
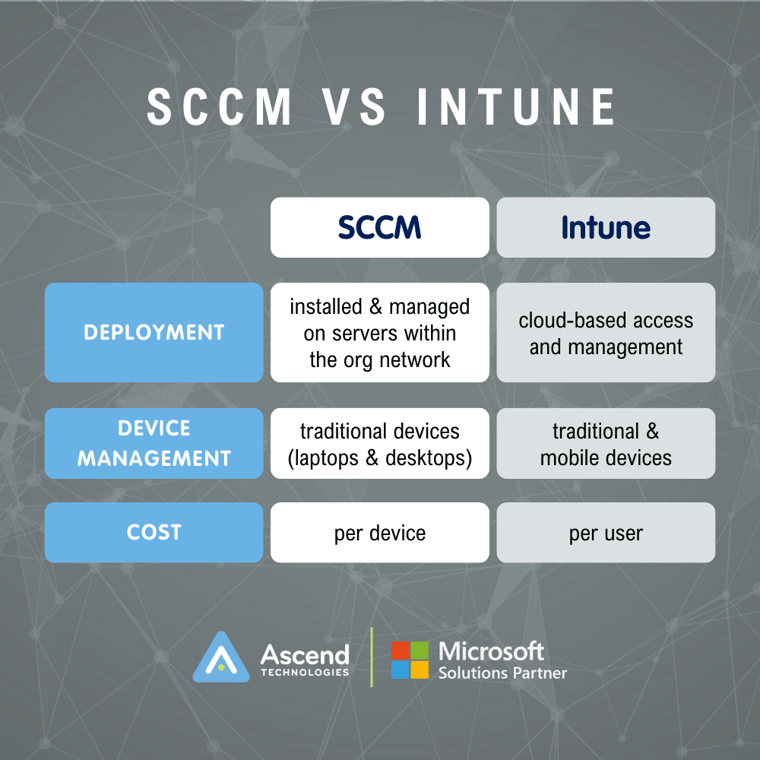
SCCM Vs. Intune: Key Differences
While SCCM and Intune serve similar purposes, there are 3 key differences we note between the two tools:
Integration with Other Tools
As mentioned earlier, Intune integrates with other Microsoft tools, such as Azure Active Directory, Office 365, and Autopilot. These integrations can transform Intune into a comprehensive device management solution.
For example:
By integrating Intune's comprehensive device management capabilities with Autopilot's streamlined enrollment process, the combined solution offers a level of automation in device provisioning that was previously unattainable. This fusion allows IT departments to minimize their hands-on involvement significantly.
Imagine the process of setting up a new device for an employee being as simple as placing an order with a vendor and marking it for Autopilot deployment. The device is pre-loaded into your Azure tenant, and upon arrival, all the end-user needs to do is switch it on. The magic begins here: the device self-configures by automatically installing the necessary software and enrolling itself with Intune after the user enters their credentials.
If that sounds like what you need, you can learn more by checking out our Digital Workspace Deployment Solution.
In contrast, SCCM is a powerful tool for on-premises infrastructure management, but it offers a different cloud-centric integration than Intune does with Microsoft's suite of tools. Depending on your organization's needs, this can result in a more siloed approach, requiring additional steps and manual intervention for tasks that Intune, combined with Autopilot and Azure AD, can automate.
Which Tool is Best for Your Organization?
Now that we have explored the differences between SCCM and Intune, you may be wondering which tool is best for your organization. The answer to this question depends on your organization's specific needs and requirements.
If your organization primarily uses traditional devices, such as laptops and desktops, and you have an on-premises infrastructure, then SCCM may be your best choice. SCCM offers many features and is a popular choice for managing large-scale deployments.
On the other hand, if your organization has a large number of mobile devices and you are looking for a cloud-based solution, then Intune may be the better option. Intune offers a range of features specifically designed for managing mobile devices and integrates with other Microsoft tools to provide a comprehensive device management solution.
Ascend Can Help
Both SCCM and Intune are powerful tools for managing and deploying software and devices in an organization. While they serve similar purposes, they have some key differences that make them better suited for different types of organizations. By understanding the differences between SCCM and Intune, you can determine which tool is best for your organization's needs and requirements.
Seeking expert advice? Contact us for a complimentary consultation to guide you through the next steps of your IT journey.

