Organizations are beginning to recognize the potential of cloud computing, and hybrid cloud strategies have become an effective tool for optimizing their IT infrastructure. By combining the benefits of public and private clouds, a hybrid cloud approach offers modern enterprises flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. It combines environments.
In this article, we'll explore the advantages of adopting hybrid cloud strategies. It provides key insights and presents recent statistics to showcase the growing importance of this strategy. Additionally, it helps readers learn how to maximize the benefits of a hybrid cloud strategy.
Table of Contents:
- The Rise of Hybrid Cloud Adoption
- What is a Hybrid Cloud Model?
- Enhancing Flexibility and Scalability
- Improved Security and Compliance
- Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
- Driving Digital Innovation
The Rise of Hybrid Cloud Adoption
A recent survey by Flexera revealed that 92% of enterprises had adopted a multi-cloud strategy, with 80% of them embracing a hybrid cloud approach. This growing trend can be attributed to the need for businesses to strike a balance between security, performance, and cost.
Using hybrid cloud strategies enables organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while maintaining the control and security of private clouds. The biggest challenge businesses face is setting up their hybrid environment to ensure they get all the benefits while mitigating the risks.
Global cloud storage is predicted to exceed 200 zettabytes by 2025, according to a prediction by Cybersecurity Ventures.
What is a Hybrid Cloud Model?
A hybrid cloud model combines public and private cloud computing environments. This approach is designed to work together seamlessly to deliver the benefits of both infrastructures. It enables organizations to optimize their IT resources by strategically distributing workloads and applications across public and private cloud platforms. This is based on specific requirements, such as security, performance, and cost-efficiency.
Now let's break that down into the benefits of both public and private to get a better understanding.
Public Cloud
Public cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), provide shared, scalable computing resources and services over the internet. These platforms offer on-demand resource access, allowing organizations to pay only for their consumed resources. Public clouds are well-suited for hosting non-critical data, handling fluctuating workloads, and deploying applications with varying resource requirements.
Some key characteristics and benefits of the public cloud include the following:
-
Multi-tenancy: Public cloud infrastructure is shared among multiple users, also known as tenants, who access resources and services independently. This shared environment helps distribute the underlying infrastructure's costs and enables efficient resource utilization.
-
Pay-as-you-go pricing: Public cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model. This allows you to pay only for the resources you consume. This also eliminates the need for upfront capital investments in hardware and software and helps organizations reduce ongoing maintenance costs.
-
Scalability and elasticity: Public cloud services are designed to scale resources up or down based on demand. This scalability allows your organization to manage fluctuating workloads efficiently and ensures that you pay only for the necessary resources.
-
Ease of deployment and management: Public cloud providers take care of infrastructure management, maintenance, and updates. This allows organization to focus on its core business operations. Users can also quickly deploy applications and services through user-friendly interfaces and APIs, reducing the time and effort required for provisioning and managing resources.
-
Access to advanced services and technologies: Public cloud providers offer a wide range of cutting-edge services and tools, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analytics, and IoT capabilities. These services enable organizations to drive innovation, create new products and services, and improve overall business performance.
However, there are also some limitations and concerns associated with public cloud services, including:
-
Data security and privacy: Storing sensitive data in a public cloud can raise security and privacy concerns. The infrastructure is shared among multiple users, and data is transmitted over the internet.
-
Compliance: Public cloud environments may not meet specific regulatory requirements, especially for organizations operating in industries with strict data protection and privacy regulations.
-
Limited customization and control: Public cloud environments offer less customization and control than private clouds or on-premises infrastructure, which may not be suitable for organizations with specialized requirements.
Despite these concerns, public clouds remain a popular choice for many organizations due to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and access to advanced technologies.
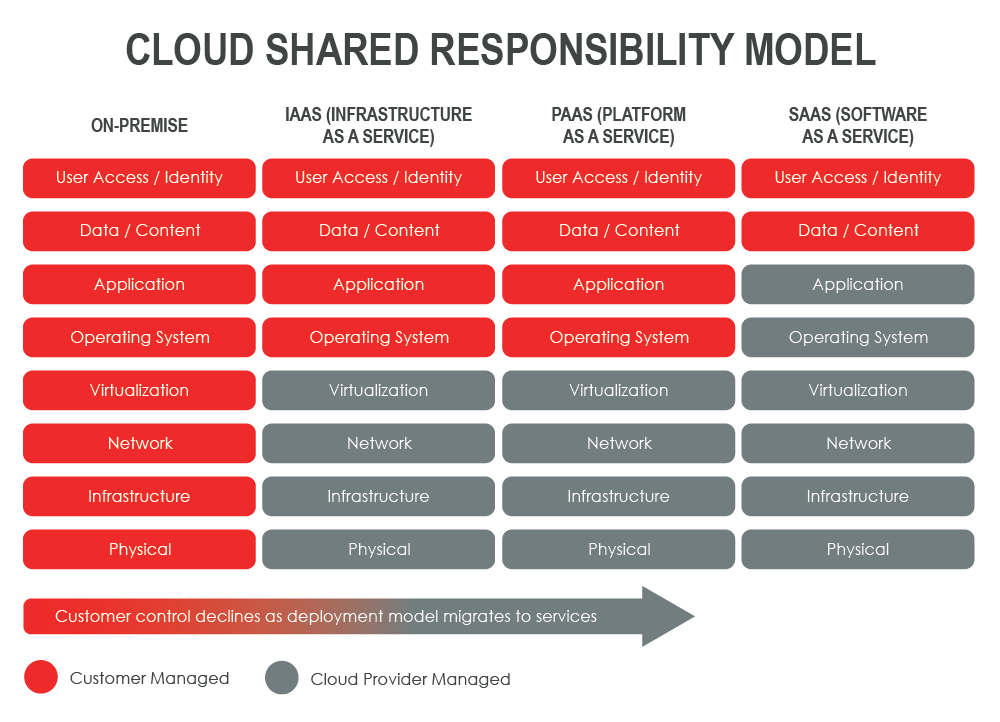
Read more about Cloud Security and the Shared Responsibility Model
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated, single-tenant computing environment that is either hosted on-premises or by a third-party service provider. Private clouds offer more control, customization, and security than public clouds. This makes them ideal for hosting sensitive data, critical applications, and meeting specific regulatory or compliance requirements.
Some key characteristics and benefits of a private cloud include the following:
- Single-tenancy: In a private cloud, the infrastructure and resources are dedicated exclusively to a single organization, ensuring complete control and isolation from other users. This dedicated environment provides greater security and privacy for your sensitive data and applications.
- Customization and control: Private clouds offer more flexibility in terms of configuring the underlying infrastructure, network settings, and resource allocation. Your organization can tailor the environment to meet your specific requirements, such as performance, security, or compliance needs.
- Enhanced security: Private clouds provide a higher level of security compared to public clouds because the infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization. This dedicated environment, combined with strict access controls and security measures, helps protect your sensitive data and applications from potential breaches or unauthorized access.
- Predictable performance: With dedicated resources and the ability to fine-tune the infrastructure, your organization can achieve more predictable performance in a private cloud environment. This allows for better resource allocation and management, ensuring optimal performance.
Enhancing Flexibility and Scalability
One of the primary benefits of hybrid cloud strategies is the ability to scale resources on-demand, accommodating fluctuating workloads and business needs. In a hybrid environment, your organization can easily move non-sensitive workloads to the public cloud during peak times while keeping critical data and applications in the private cloud. This flexibility ensures that businesses can quickly adapt to changing market conditions, ultimately driving efficiency and competitiveness. Here, we explore various ways organizations can enhance these aspects within a hybrid cloud environment.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Models:
Choosing the appropriate cloud service models is critical to optimizing flexibility and scalability. The three primary service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. Users manage operating systems and applications while the provider handles the infrastructure. Some examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for building, testing, and deploying applications, including middleware, development tools, and runtime environments. It simplifies application development and deployment. Some examples include Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, Heroku.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access them via a web browser. The provider manages infrastructure, updates, and security. Some examples include: Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace.
By identifying the models that best suit your needs, your organization can leverage the cloud's full potential and gain greater control over your resources.
Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting is a technique that allows businesses to move workloads between private and public clouds dynamically. During periods of high demand, applications running in the private cloud can "burst" into the public cloud to access additional resources. This approach enables organizations to scale resources seamlessly, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Containerization and Microservices
Adopting containerization and microservices can greatly enhance flexibility and scalability in a hybrid cloud environment. Containers are lightweight, portable units that encapsulate applications and their dependencies, making deploying and managing them easy across different cloud environments. Microservices break applications into smaller, independent components that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Together, these approaches enable your organization to respond quickly to changing demands and scale resources more efficiently.
Implementing Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration tools can help you manage your hybrid cloud environments more effectively, reducing manual processes and improving scalability. These tools can automate tasks such as resource provisioning, load balancing, and application deployment, ensuring that resources are allocated and managed efficiently. Additionally, orchestration tools can help coordinate complex workflows across multiple cloud environments, streamlining operations and enhancing overall agility.
Monitoring and Analytics
Proper monitoring and analytics are crucial for maintaining flexibility and scalability in a hybrid cloud environment. By collecting and analyzing data from both public and private clouds, your organization can gain insights into resource usage, application performance, and potential bottlenecks. Armed with this information, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation and scaling, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Opting for a Multi-Cloud Strategy
A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple public cloud providers, offering even greater flexibility and scalability. By leveraging the strengths of different cloud providers, your organization can access a broader range of services, reduce vendor lock-in, and minimize the risk of downtime due to provider-specific issues. This approach enables you to optimize your hybrid cloud environment, taking advantage of the best features and capabilities each provider has to offer.
Overall, enhancing flexibility and scalability in a hybrid cloud environment involves a combination of strategic planning, technological adoption, and effective management. By implementing these tactics, organizations can create a dynamic and agile infrastructure that adapts to changing business needs and drives long-term success.
Improved Security and Compliance
When set up correctly, hybrid cloud strategies provide your organization with enhanced security and compliance capabilities. By keeping sensitive data and applications in a private cloud, you can maintain control over their IT infrastructure and ensure regulatory compliance. Additionally, using encryption, access controls, and advanced monitoring tools can help minimize the risk of data breaches and cyber threats.
Data Classification and Segregation
Proper data classification and segregation are essential for maintaining security and compliance in a hybrid cloud environment. By identifying and categorizing data based on sensitivity and regulatory requirements, your organization can determine which data should remain in the private cloud and which can be safely stored in the public cloud. This approach ensures that sensitive information remains under your control, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Strong Access Controls
Implementing robust access controls is crucial for securing data and applications in a hybrid cloud environment. Organizations should establish strict user authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identity of users accessing cloud resources. Additionally, implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that your users are granted access only to the resources necessary for their job, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and data leakage.
Data Encryption
Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is vital for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining compliance. Organizations should adopt robust encryption algorithms and encryption key management practices to protect data across their hybrid cloud environment. By encrypting data before it leaves the private cloud, You can ensure that it remains secure even when stored in the public cloud.
Regular Security Assessments and Audits
Conducting regular security assessments and audits helps organizations identify potential vulnerabilities in their hybrid cloud environment and take corrective actions. Security assessments should include penetration testing, risk assessments, and cloud security configuration assessments. Regular audits can also help you ensure adherence to compliance requirements and identify areas for improvement.
Centralized Security Management
In a hybrid cloud environment, security management can be challenging due to the complexity of multiple cloud platforms. Implementing a centralized security management system can help your organization monitor and manage security policies, access controls, and compliance requirements across your entire hybrid cloud infrastructure.
This can be done in-house or through a Cloud Security Posture Management provider. This approach simplifies security management, improves visibility, and enables businesses to respond more effectively to potential threats.
Partnering with the Right Cloud Providers
Choosing cloud providers with robust security features and a solid commitment to compliance is crucial for maintaining a secure hybrid cloud environment. Your organization should evaluate potential providers based on their security certifications and their adherence to industry-specific regulations. Additionally, partnering with a cloud solution provider is another way to help organizations protect their data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
According to a report released by Checkpoint, the top 3 cloud security concerns are misconfiguration, unauthorized access, and insecure API. To ensure your cloud security concerns are addressed, we recommend you talk to an expert.
Improving security and compliance in a hybrid cloud environment requires a combination of strategic planning, technology adoption, and effective management. By implementing these strategies, your organization can protect sensitive data, maintain regulatory compliance, and build a strong foundation for your hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
Cloud cost optimization has been a focus for five straight years, with 61% putting it as their top priority, according to a report published by Flexera. Organizations can optimize resource usage and reduce overall IT costs with a hybrid cloud approach.
Businesses can minimize waste and lower expenses by only paying for the resources they consume in the public cloud. Furthermore, quickly scaling resources up or down allows organizations to avoid wasted costs and resources. The three main factors contributing to cost and resource optimization are the pricing model, the ability to auto-scale, and the reduced footprint.
Pay-As-You-Go Pricing Model
Public cloud services typically operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing you to pay only for the resources consumed. This model eliminates the need for upfront capital investments in hardware and reduces ongoing maintenance costs.
Auto-Scaling and Elasticity
Hybrid cloud environments can automatically scale resources up or down based on real-time demand. This auto-scaling feature helps your organization optimize resource utilization and reduce costs by ensuring you only pay for what's needed.
Reducing Data Center Footprint
By migrating workloads and applications to the public cloud, your organization can offload the need for maintaining physical hardware, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment. This reduction in on-premises hardware allows companies to minimize the physical space and power consumption required for data center operations.
Check out this article for a walkthrough of evaluating your cloud for cost optimization.
Driving Digital Innovation
Embracing a hybrid cloud strategy is an essential step in the digital transformation journey for many businesses. By enabling organizations to leverage cutting-edge technologies and services, hybrid cloud strategies can accelerate innovation and enhance overall business agility.
Faster Time-to-Market
Hybrid cloud environments enable you to develop, test, and deploy applications more quickly by providing easy access to resources and tools. The ability to scale resources on-demand in response to changing requirements helps your organization bring new products and services to market faster, giving you a competitive advantage.
Improved Collaboration and Agility
By leveraging both public and private cloud resources, teams can collaborate more effectively across different locations and departments. In addition, hybrid cloud environments facilitate the sharing of data, applications, and resources, allowing your teams to work together seamlessly and quickly adapt to changing business needs.
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies
Hybrid cloud models give your organization access to the latest technologies and services public cloud providers offer. These services may include advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT capabilities, which can drive digital innovation by enabling you to create new products, services, and business models.
Enhanced Data Analytics and Insights
By consolidating data from various sources in a hybrid cloud environment, you can leverage powerful analytics tools available in the public cloud to gain valuable insights. These insights can help drive data-driven decision-making and innovation by uncovering trends, identifying opportunities, and optimizing operations.
Ascend Can Help
Hybrid cloud strategies are quickly becoming the go-to approach for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure. By providing the perfect blend of flexibility, security, and cost-efficiency, hybrid cloud environments enable you to navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape confidently. If your organization is considering a hybrid cloud strategy or looking to optimize your existing hybrid environment, now is the time to explore the possibilities and unlock the full potential of this powerful approach.
Reach out and talk to an expert to get started today!